THe History of building with Bricks
BUILDING WITH BRICKS
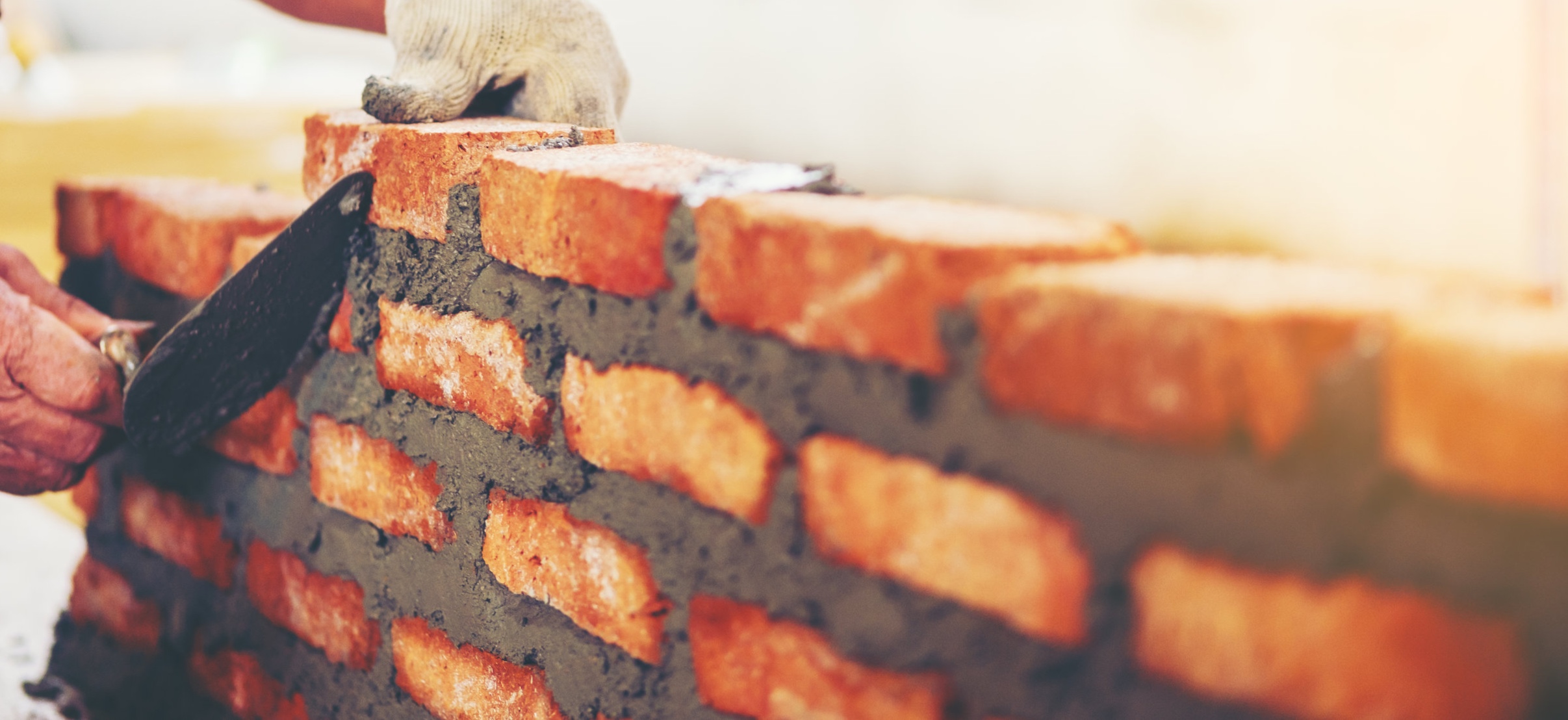
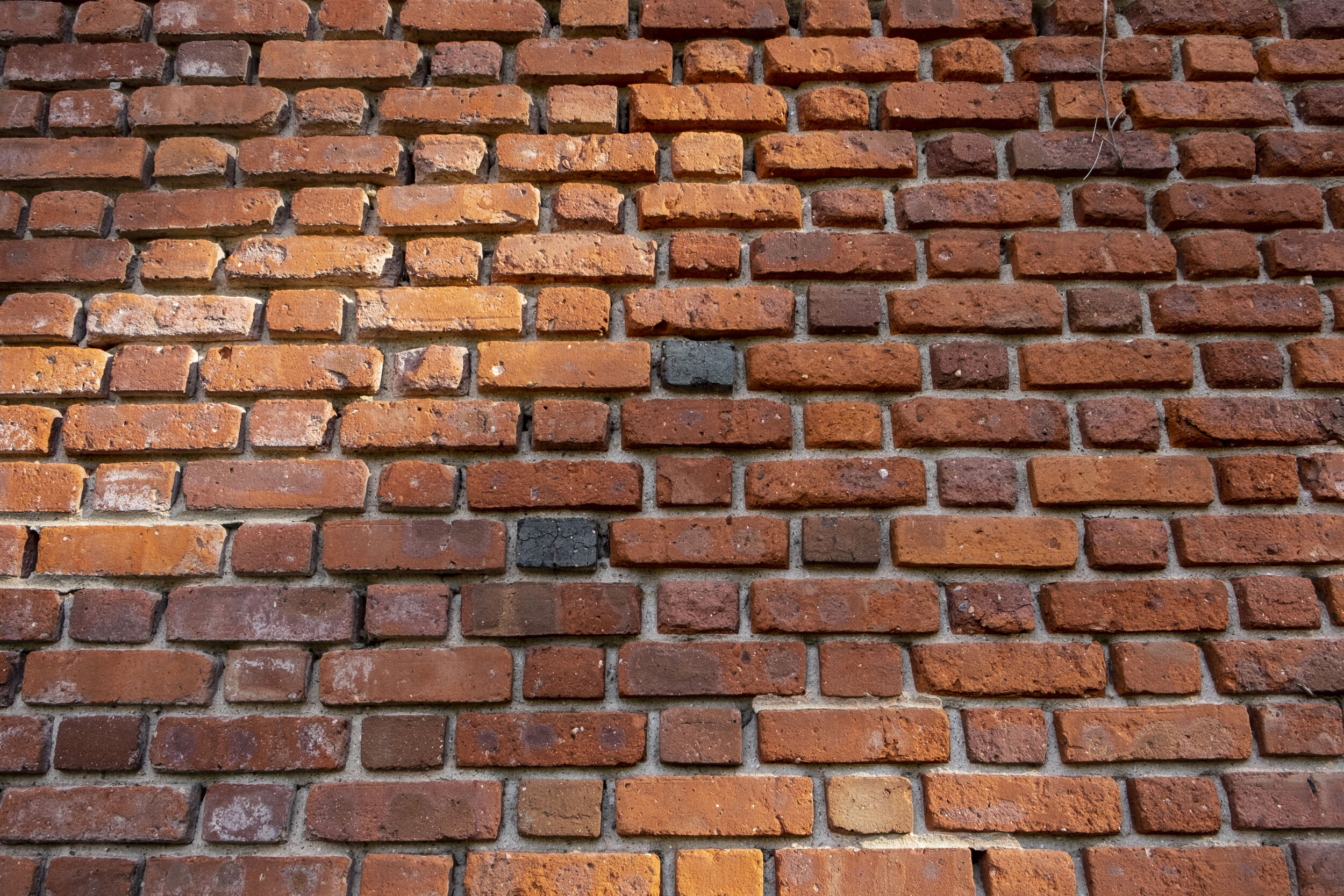
The indented center Face of a Brick is called the “FROG”. Brick factories imprinted their logos onto the FROG, giving each factory a unique identification that are now sought after by collectors and historians today.
An abundant natural resource, bricks are made from clay sediment called Varve Clay [vahrv kley], consisting of hydrated silicates of aluminum found in lake sediment and river beds. One of the oldest materials for building, architecture made with bricks have been dated back to 7,000 BC at archeological dig sites. Buildings made from bricks are environmentally friendly and energy efficient because they are heat resistant and non permeable to high pressure and frost.
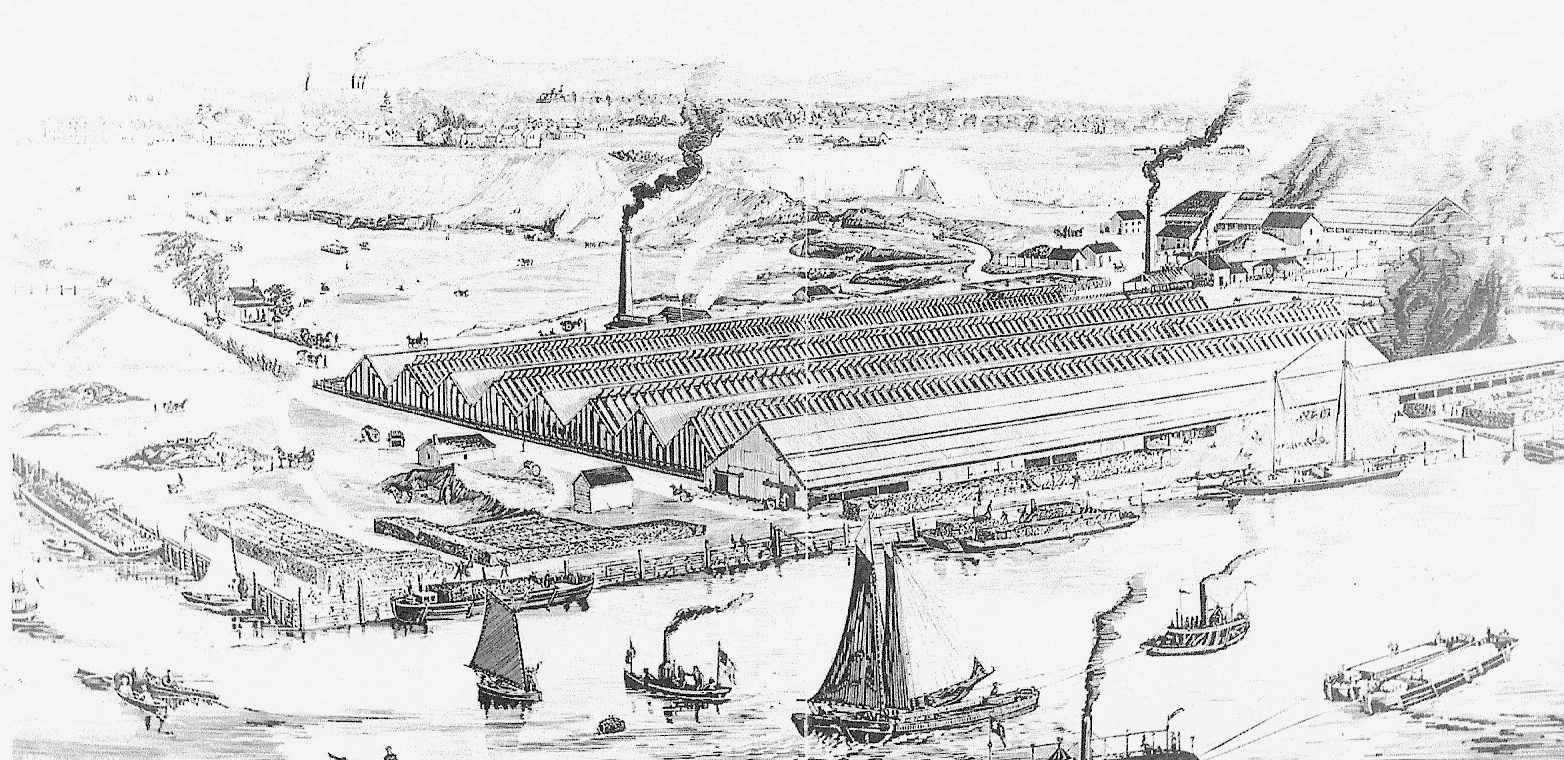
Ice Age glaciers deposited huge amounts of clay along the banks of the Hudson River, making the Hudson Valley an important resource for early Dutch settlers to the Americas and the North Rockland region the center of the Brick making industry from the 1700’s to the 1940’s.
In 1835, the Wall Street Fire devastated 674 buildings and 13 acres of New York’s financial district, leading to a change in building codes increasing demand for buildings made with bricks. Thanks to the Hudson River, Haverstraw’s brick makers were well positioned to supply New York’s exploding demand for bricks.
Go therefore now and work; for there shall no straw be given to you; yet ye shall deliver the tale of bricks.
Exodus 51-8
IMPORTANT BRICK TERMS
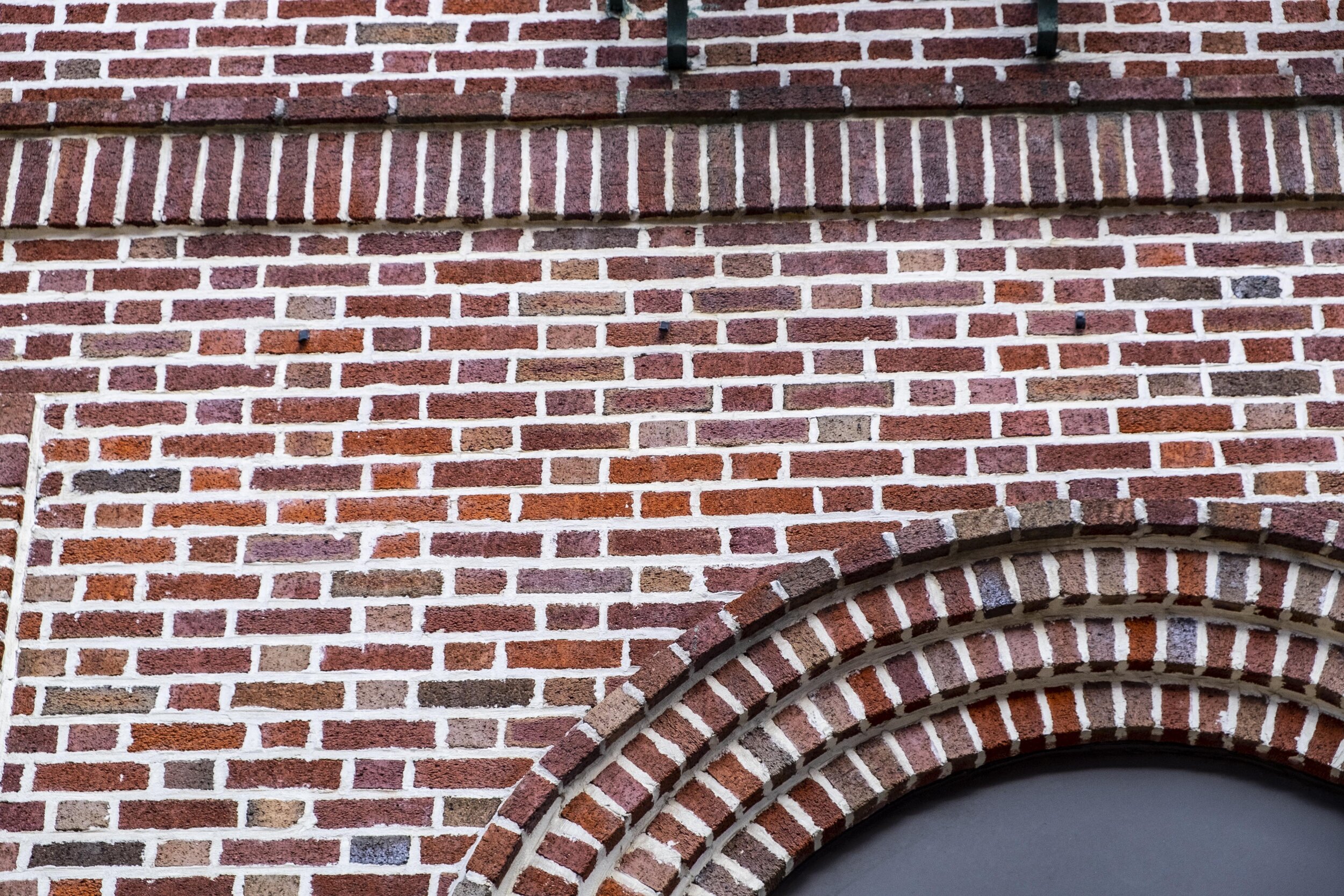
BOND
The patterned arrangement of brick or stone in a wall
MORTAR
A pasty building material composed of sand, lime and cement mixed with water. This mixture gradually hardens when exposed to the air. Mortar is used as a joining medium in brick and stone construction.
JOINT
The mortar bond placed between individual masonry units such as brick, block or stone.
COURSE
A horizontal row of bricks, when laid in a wall. It is a continuous level or layer of any masonry unit throughout the face or faces of a building. A header course, for example, would consist entirely of header facing bricks.
The brick yards of John Derbyshire, Cole 1884
Cutting the clay for bricks, Haverstraw, NY
Structural Brick Bonds
Brick walls can be structural, like load bearing walls, or they can also be primarily decorative, like a brick-veneer wall. Structural walls demand solid structural bonds, while decorative walls can use any bond pattern.
One of the most commonly utilized variations of brick bonds in masonry works. This bond essentially comprises of alternating courses of headers and stretchers. Headers are laid centred over the stretchers in the course below and each alternate row is vertically aligned. To break the continuousness of vertical joints, a quoin closer is used at the start and end of a wall after the first header. A quoin close is a brick that is cut lengthwise into 2 halves and used in the corners in brick walls. This type of bond is mainly used to construct stronger walls that are one brick thick.
TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE
PLAY THE BRICK BOND GAME
This bond features a header course every 5th, 6th or 7th course
For this type of bond, each course is made up of alternate headers and stretchers. Each header is centered on a stretcher above and below and every alternate course begins with a header in the corner.
One of the most common brick bonds, also popularly called “running bonds”. This bond is very easy to lay, in fact, is one of the simplest ones used today. Stretcher bond is suitable when walls of half brick thickness need to be constructed.
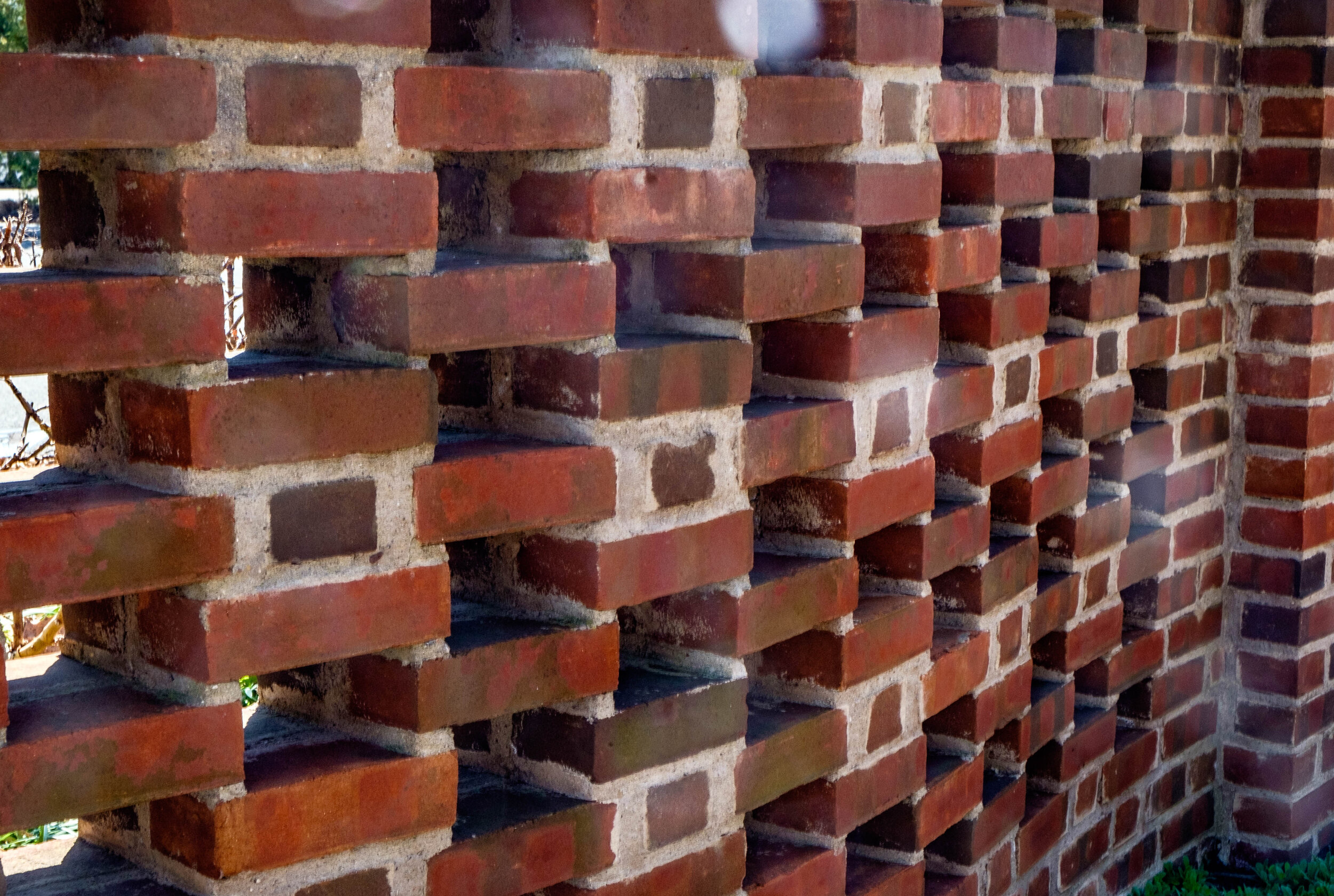
The herringbone bond is a non-structural decorative bond and imitates a herringbone weave with a distinctive v-shaped pattern
A header is the shorter face of the brick. In header bond brick masonry all bricks are constructed in the header course. In this bond, the overlap is performed corresponding to a half width of the bricks. The three-quarter brickbats are utilized in alternative courses as quoins. This bond is mainly used for the construction of one brick thick walls.